
Background:
HQ-Mozambique was launched in 2006, and QI activities have now been embraced as a primary national strategy of health systems strengthening in the HIV service sector. QM processes are now being integrated into clinic management and are a key strategy of the MOH HIV care and treatment health sector strategic plan, an effort characterized by the transition from HIVQUAL to CLINIQUAL in expansion of quality across the health sector.
In 2009, the Minister of Health announced the integration of HIV and primary care to reduce stigma and assure care availability at the local level. In 2010, all health facilities providing ART were integrated into primary care, with decentralization of large “day hospitals” and patients referred back to primary health care centers.
HEALTHQUAL activities in Mozambique have been expanded to all 11 provinces (from the initial 9), with provincial teams charged with overseeing and supporting all HIV and non-HIV quality activities within their provinces.
This new model has been launched first in 5 provinces, with teams trained in mid-2010, with the remaining 6 province teams trained shortly after. The provincial teams, once trained, will be responsible for the expansion of HQ to the districts within their provinces.
HIV/AIDS Epidemic:
Mozambique has a population of approximately 22 million people with a life expectancy of 41.2 years at birth.[i],[ii] In 2007, national HIV prevalence was 12.5%.[iii] More recent data have not yet been released, but an estimated 1.5 million individuals are living with HIV/AIDS.[iv] It is estimated that at least 100,000 children <15 years are living with HIV.[v]. Approximately 90,000 people are currently prescribed ART.[vi] Disparities in access to treatment are geographically evident, with 60% coverage in Maputo City and Maputo Province, 34% in the southern region, 11% in the central region and 6% in the northern region.[vii] Accordingly, the Minister has mandated simultaneous implementation of HQ across the country to address this inequity. The majority of HIV care is provided at the health center level, 183 of the 215 treatment facilities, with the remainder at hospitals.
Demographic Data:
- Population: 20 million
- HIV Prevalence: Adult (15-49) 11.5%
-
Children≤5 years – 2.2%
-
Children 12-14 years – 1.8%
-
Children 15-19 years – 5.0%
-
Southern region has highest prevalence at 21%;
-
Northern region lowest prevalence at 9%;
-
Southern region has high prevalence due to high urban population density (multiple concurrent partnerships) and frequent migration with South Africa for work in the mines;
-
TB/HIV prevalence: 60%
-
Illiteracy rate is roughly 60%
-
HIVQUAL began in late 2006
-
Initially adult HIV only
-
Pediatrics and PMTCT beginning in 2010
-
-
Currently 108 clinics with expansion planned to most clinics providing ART
Mozambique Health System Infrastructure:
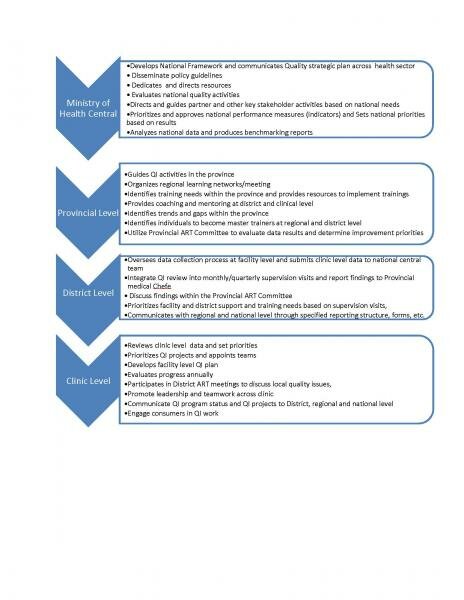
Mozambique operates a centralized public health care system organized into 11 provinces and supported by multiple implementing partners. Within the Ministry of Health in Mozambique (called the Ministério de Saúde or MISAU) there are 3 levels of organization; national, provincial (provincial health departments, DPS), and district. The minimum level of health care is provided at health posts in Mozambique. Following health posts, health care can be obtained at health centers, rural hospitals, provincial hospitals, or central hospitals. Mozambique has a central hospital located in each region (Maputo, Beira and Nampula).
HQ-Mozambique engages provincial medical chefes, who oversee quality of all health care in their respective provinces. They are afforded autonomy and flexibility in determining strategies to accomplish this goal.
[i] World Bank, World Development Indicators
[ii] CIA, The World Factbook, accessed on 01/11/10 at https://cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/mz.html
[iii] UNAIDS, 2008. Accessed at: http://www.unaids.org/en/default.asp
[iv] Epidemiological Fact Sheet on HIV and AIDS: Mozambique UNAIDS/WHO/UNICEF (updated 2009)
[v] Epidemiological Fact Sheet on HIV and AIDS: Mozambique UNAIDS/WHO/UNICEF (updated 2009)
[vi] UNAIDS, 2008. Accessed at: http://www.unaids.org/en/default.asp
[vii] UNAIDS, 2008. Accessed at: http://www.unaids.org/en/default.asp




- CLINIQUAL Mozambique clinics have collected 5 rounds of data reviewing care provided from January 2007 through December 2012
- During the most recent round of data collection, Mozambique collected the second round of data for pediatric indicators
- 195 CLINIQUAL Mozambique clinics have participated in HEALTHQUAL data collection, sampling 41,199 total charts
- Performance rates have been measured for the following 11 indicators: Visits (3 different measures), CD4 monitoring (4 different measures), ARV therapy (1st and 2nd line), adherence (5 different measures), CPT, TB clinical screen, TB diagnostic evaluation, extra pulmonary TB screen, IPT, referrals for TB care, TB medication documentation, prevention education, post-exposure prophylaxis, WHO clinical staging, psychomotor development and nutrition indicators (weight, height, weight for height)
- Here we show data for the following indicators: clinical visits, CD4 monitoring, ARV therapy, adherence assessment, CPT, prevention education and TB clinical screen as well as the following pediatric specific indicators: WHO clinical staging, psychomotor development. weight, height and weight for height
